|
The program
PASS predicts ca. 5000 biological
effects using as input 2D structures in the form of an SDFile. The
accuracy of prediction is high and proven in many publications.
Convince your-self and submit a molfile using the online version for
free:
http://ibmc.msk.ru/PASS.
PASS was
developed to solve the problem that it is practically impossible to test
experimentally a compound for all possible biological activities.
We use
PASS to find selectively compounds that
show a desired biological activity. For this we need clustering
techniques and other programs that develop descriptors, such as
fingerprints to present the most interesting structures to the
researcher.
We present with CWM Lead Finder an
application that allows the
researcher to find new active compounds that are similar in biological
activity to a set of compounds with known biological activity, but not necessarily similar in
structure.
For this we need an SDFile with compounds of known activity
(KNOWNS),
let's chose Alzheimer Treatment, and a SDFile with
compounds of untested effects (UNKNOWS). We predict all the
PASS
coefficients Pa-PI for the KNOWNS. Most of the activities
have values around zero, and are noise. We select those activities that
show for the largest number of compounds highest coefficients. This
subset of activities we consider to be the "biological profile".
Using this subset of activities we predict the PASS coefficients for the
UNKNOWNS. We cluster the profiles, and select those compounds that
appear in clusters of KNOWNS and UNKNOWNS. We calculate fingerprints;
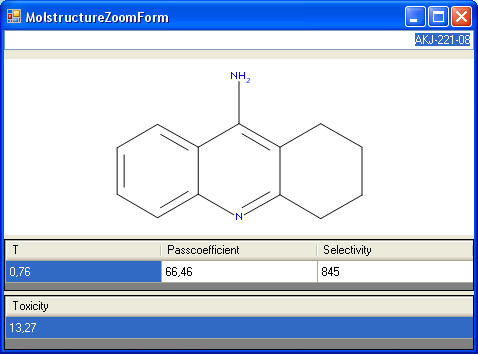
this allows us to sort by structure similarity - value "T" in the
picture to the right. We sum the
PASS
coefficients for each compound "Passcoefficient"; this is a measure how well the compound
fits the biological profile. We display the number of
possible activities of Pa >Pi, "Selectivity"; this is measure how selective the
compound is. Small compound show often effects for a lot of activities,
but are not very interesting compounds for drug research. We calculate
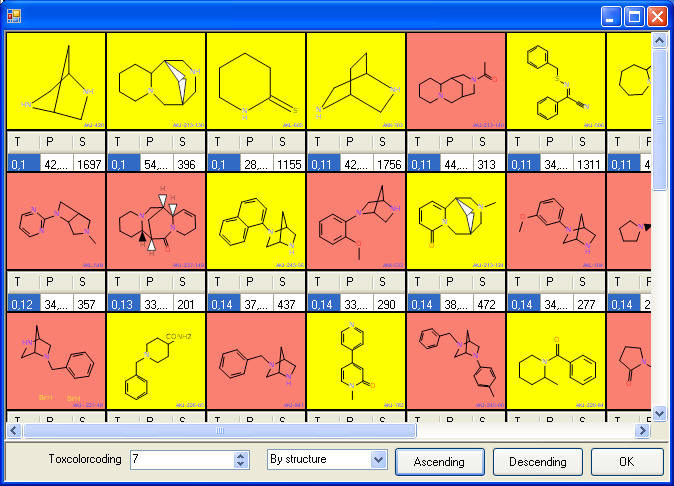
the PASS parameters for about 40 toxicities and color code compounds by
yellow if the are above a selected threshold.
As result we show the compounds that are
predicted in a grid, and the researcher can sort by structure - the most
dissimilar structures of the UNKNOWNS compared to the KNOWNS might be
most interesting. He can sort additionally by profile similarity and "selectivity".
|
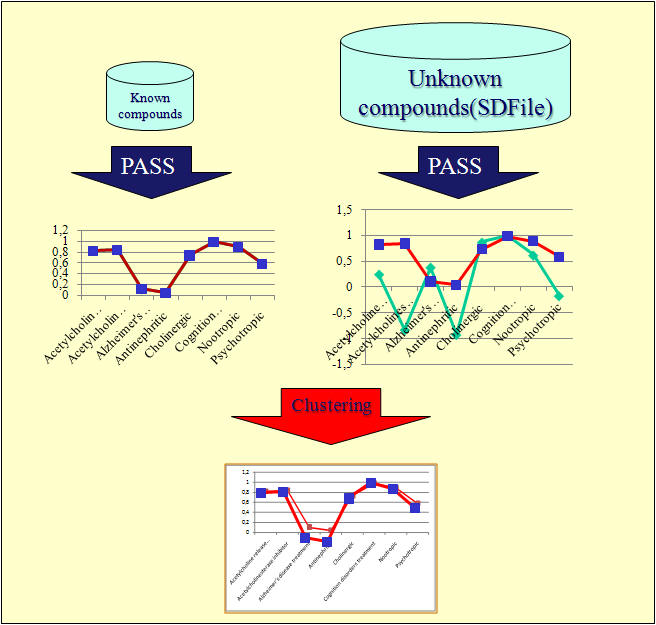
The CWM Lead Finder
matches compounds of unknown activities according to their biological
profile to compounds of known biological activities.
|
The x-axis on the graphs above
shows biological effects, such as nootropic, the y-axis is the measure
for prediction.
1 means that PASS is 100% confident that a compound
shows such an effect, -1 means
PASS predicts that the compound does
not have this effect.
|
|
|
CWM Lead Finder
Software to evaluate quickly with
minimum user interaction a database of untested compounds for
leads.
|
|
CWM Global
Search
Search Internet by chemical structure, combining Google, PubChem,
eMolecules, ChemSpider, etc. |
|
CWM Tox Predictor
Research project to combine
several tox models to see if the answers of different model
converge to predict toxicities with high reliability
|
Finding new potential acetylcholine esterase
Inhibitors in SDFiles using CWM Lead Finder
and PASS (Prediction of Activity Spectra for
Substances)
Hans-Jürgen Himmler and
Alexander Kos
AKos Consulting & Solutions Deutschland
GmbH (AKos GmbH), Austr. 26, D-79585
Steinen, Germany
corresponding author email: software@akosgmbh.de
from 3rd German Conference on
Chemoinformatics
Goslar, Germany. 11-13 November 2007
Chemistry Central Journal 2008,
2(Suppl 1):P42doi:10.1186/1752-153X-2-S1-P42
The electronic version of this abstract is
the complete one and can be found online at:
http://www.journal.chemistrycentral.com/
content/2/S1/P42
|
|
|
We created a completely diverse database
of 329 compounds from 2.4 million. 303 compounds could be computed by
PASS. We
seeded this set of compounds with 9 compounds from
Symyx Drug Data Report (MDDR) database
with known Alzheimer treatment activity. As KNOWNS we used 21 drugs on
the market from the database
Comprehensive Medicinal Chemistry (CMC).
CWM Lead Finder found as only hits 5 compounds of the 9 from MDDR. This
proved that CWM Lead Finder can find with high selectivity compounds
that have a desired biological activity.
We tested CWM Lead Finder presently
mainly with databases in the size of 5000 compounds. If you are
interested to participate in the CWM Lead Finder-beta testing, please let us know and
send an email to
akos@akosgmbh.de.
On more comment for people that have
experience with
PASS.
If your desired effect is not yet incorporated in
PASS, you
had to train PASS with your own data, provided you had enough data. The
CWM Lead Finder overcomes this problem. However, even we cannot do
wonders and the knowledge base of PASS has to be trained with some
related effect. However, this related effect needs not to be known by
you. |
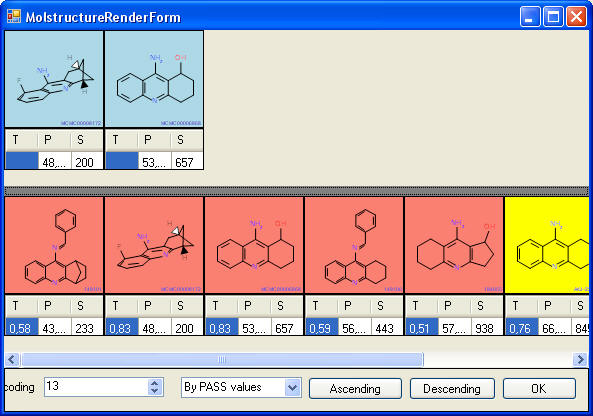
This screenshots shows the clusters, cluster that
contain "Known" and "Unknown" are color coded.
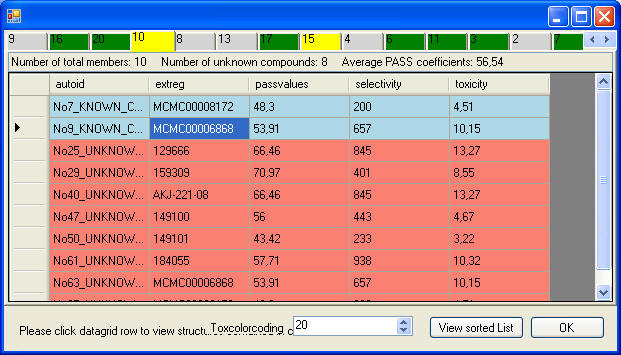
This screenshot shows ths members of one cluster,
teh blue ones are the "Knowns", the red ones the "Unknowns", and
structures with potential toxicity are colored yeallow.
|
For evaluating and purchasing CWM Lead
Finder, please contact us at software(at)akosgmbh.de. |
|
|
Poster presentation
Finding new potential acetylcholine
esterase Inhibitors in SDFiles using CWM Lead Finder and PASS
(Prediction of Activity Spectra for Substances)
Hans-Jürgen Himmler
and Alexander Kos
AKos Consulting & Solutions Deutschland GmbH (AKos
GmbH), Austr. 26, D-79585 Steinen, Germany
corresponding author email
from 3rd German
Conference on Chemoinformatics
Goslar, Germany. 11-13 November 2007
Chemistry Central Journal
2008, 2(Suppl 1):P42doi:10.1186/1752-153X-2-S1-P42
The electronic version of this abstract is the
complete one and can be found online at:
http://www.journal.chemistrycentral.com/content/2/S1/P42
|
|